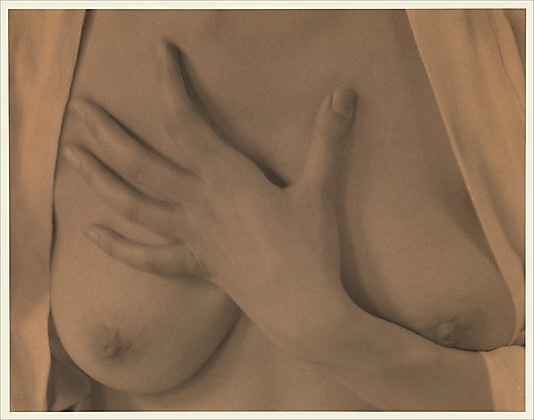
The distinctive trashy glamour of Egon Schiele’s nudes is unsettling and alluring at the same time, provocative and eye-catching. His drawings and watercolours of skinny, fragile, starved nymphets who look like they live on lipgloss and cigarettes, made from 1910 to about 1914/15, before the war and before his marriage, encapsulate the heroin chic aesthetic decades before was defined and popularised by models such as Kate Moss. Things that connect these drawings and watercolours are the same mood and aesthetic and the same reaction from the public. Schiele’s portrayal of female form was shocking to the early twentieth century Vienna, and photographs of Kate Moss’s skinny body received the same reaction.
 Kate Moss by Corinne Day
Kate Moss by Corinne Day
In the beginning of this year I watched a new documentary about Egon Schiele called “Egon Schiele: Dangerous Desires (2018)” made to commemorate the 100th anniversary of his death. It which was super cool and I loved it to death, it was hard not to like it: the soundtrack was rock music and the first lines were spoken by Iggy Pop, who clearly appreciates Egon Schiele’s art. One woman says something really interesting in the first two minutes: “If someone were to show you a Schiele watercolour and ask you: ‘when do you think this was done’, I think the answer would be: yesterday.” I partly agree; as a nostalgic person who romanticises the past, I would never believe that something as great could have been painted yesterday, but I agree in that his drawings, great majority of his art, appears not modern but timeless.
I can’t really say “modern” because Schiele wouldn’t agree. In one of his watercolours from prison he wrote: “Kunst kann nicht modern sein; Kunst ist urewig.” or “Art can not be modern, art is primordially eternal.” I don’t think this can be said about all art, but Schiele truly succeeded in creating art that is eternal. When you look at it now, it doesn’t seem out of place, kitschy, or strange, on the contrary, those colours and lines on papers that he held in his hand sometime in 1912 still have so much to say – or scream. And Schiele’s art goes so well with modern music as well, rock music particularly; in his self-portraits of the tormented artist staring right at us from the canvas, you can imagine a streetwise yet vulnerable heroin addict from the song “I’m waiting for the man” by The Velvet Underground, or the raw and trashy sound of The Stooges’s “Raw Power” or the sleek sound of urban alienation from David Bowie’s Berlin-era albums.

Egon Schiele, Nude against coloured background, 1911
I like Schiele’s paintings, and I also enjoy looking at pictures of Kate Moss, particularly those from the 1990s, it’s just an aesthetic thing, I don’t care for her personality or her life choices, although her love life is interesting. I look at a picture only to get a shot of beauty in my veins and possibly a seed to inspire my future reveries. I am certain that Kate Moss would be a perfect model for Schiele. His ideal was a thin, fragile, bony body with that elegantly wasted look; protruding spine and collar bones, under eye circles, ribs peeking under thin layer of skin, strange complexion with patches of unnatural colour…. The heroin chic look that Schiele clearly painted decades before, has become synonymous with Kate Moss whose appearance at the beginning of her career was in stark difference to the perfect and unattainable looks of the supermodels of the previous decade. Calvin Klein spoke in her defense back in the day: “For them, what is real is beautiful—looking plain is beautiful. What is less than perfect is sexy.” Schiele liked strangeness and imperfections and never resorted to idealization.
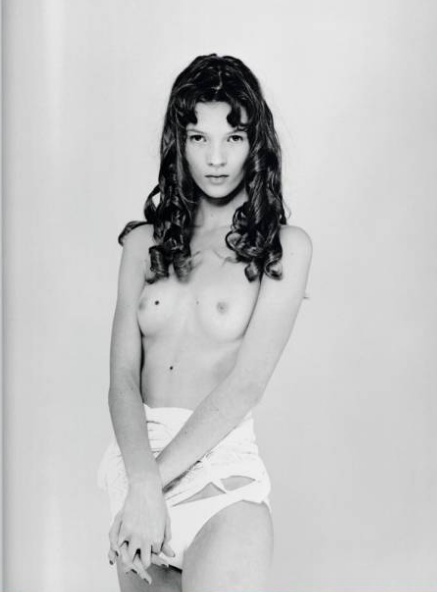

Kate Moss by Bettina Rheims, 1989

Egon Schiele, Girl with black hair, 1910
Schiele’s models were often girls from the streets, pretty prepubescent street urchins hungry for attention and amusement. He was young and poor and probably couldn’t even afford a proper model, and why would he when these little things were around, looked and behaved unpretentiously and were a good thing to draw. In his book about Egon Schiele, F. Whitford wrote: “Physically immature, thin, wide-eyed, full-mouthed, innocent and lascivious at the same time, these Lolitas from the proletarian districts of Vienna arouse the kind of thoughts best not admitted before a judge and jury.” The same words could be used to described the teenage Kate Moss; thin, wide-eyed, with full lips and gorgeous high cheek bones, on the pictures taken by Corinne Day for The Face magazine in 1990 she looks innocent and vulnerable, a bit shy, hiding herself behind a straw hat. In 1990 this working class nymphet from Croydon, a drab suburb of London, had already left school, and despite being a rich and famous model today, back then the prospects were bleak and she was in a similar position as the street urchins who posed for Schiele. Her beauty wasn’t yet recognised, but she did attract the attention of some designers very early on such as John Galliano who chose her for his spring/summer collection 1990 and saw her as his “Lolita”; the half-child and half-woman appeal made her stand out.

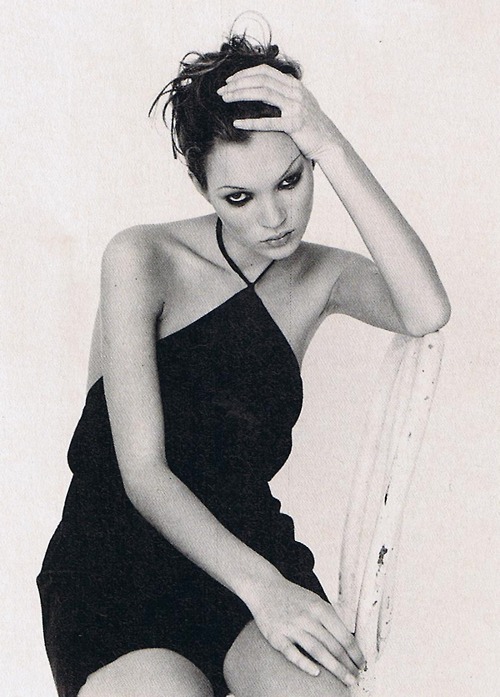
Kate Moss for Calvin Klein

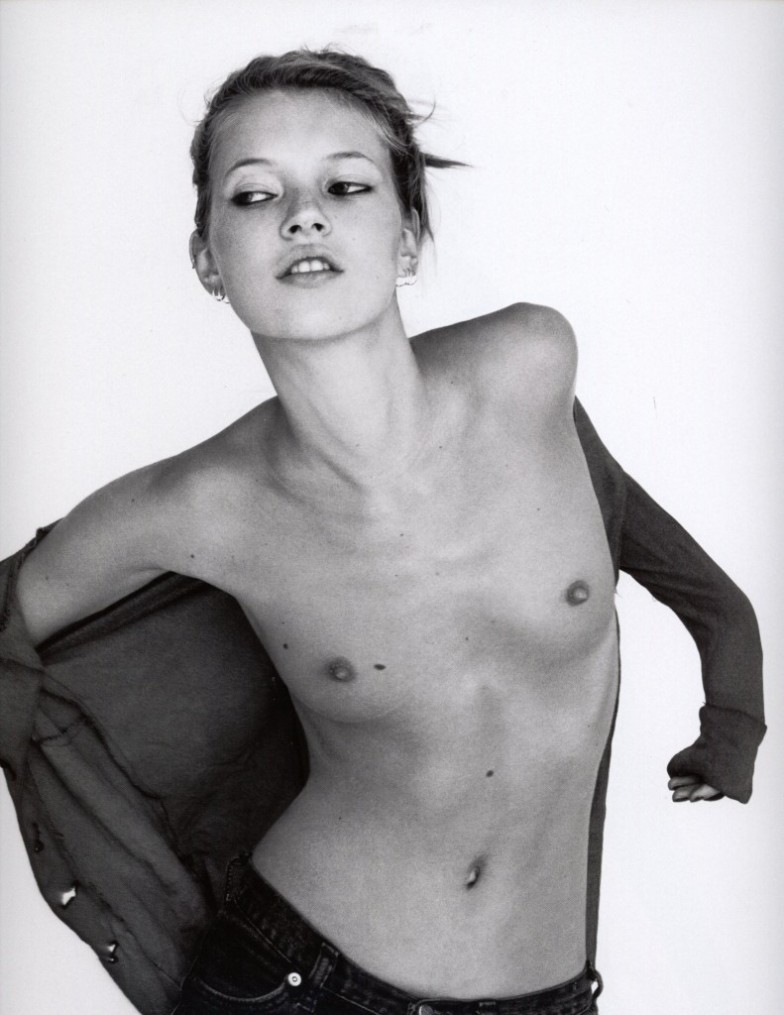
Kate Moss by Corinne Day, 1993


Egon Schiele, Sitting girl with ponytail (Sitzendes Mädchen mit Pferdeschwanz), 1910
Schiele’s drawings were outrageous and provocative in his day and age just as they are now still. Viennese public had perhaps grown accustomed to Klimt’s nudes, but the vision of the female form that Schiele had presented was a tad too much. Likewise, pictures of Kate shot in the early nineties by a young and ambitious autodidact photographer Corinne Day were considered equally outrageous and accused of perplexing ideas that neither Kate nor Corinne had dreamt of; in the pictures she looked skinny and childlike, but her clothes and poses weren’t childlike at all, mingling sexuality with innocence. Kate Moss’s appearance represented the nihilistic spirit of the decade and a culture that believe in nothing. Hippies had hope, acid and belief in a better world, punks had their anger and outrageous clothes, and nineties seemingly had nothing, to quote Manic Street Preachers: “I know I believe in nothing, but it’s my nothing”.
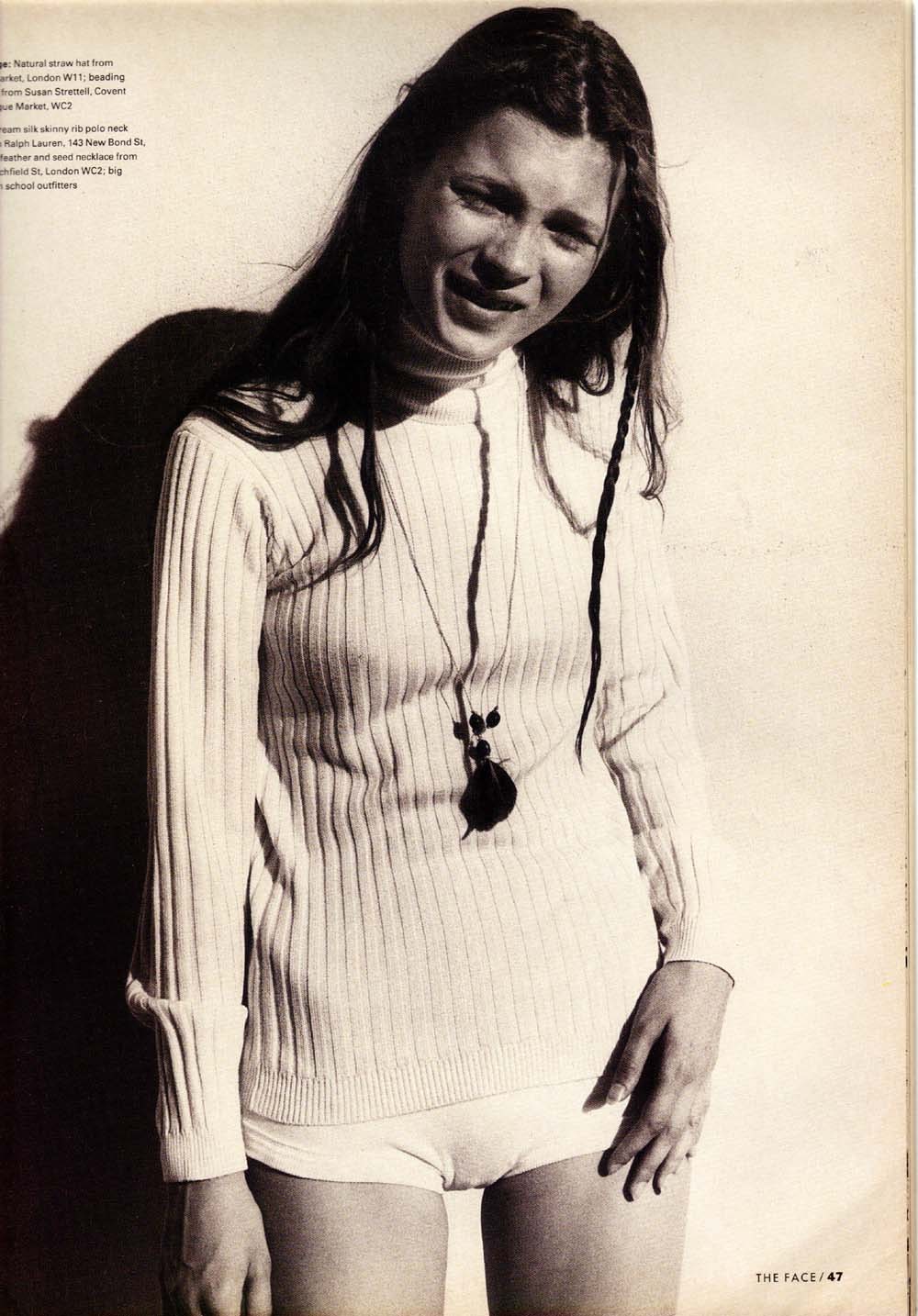
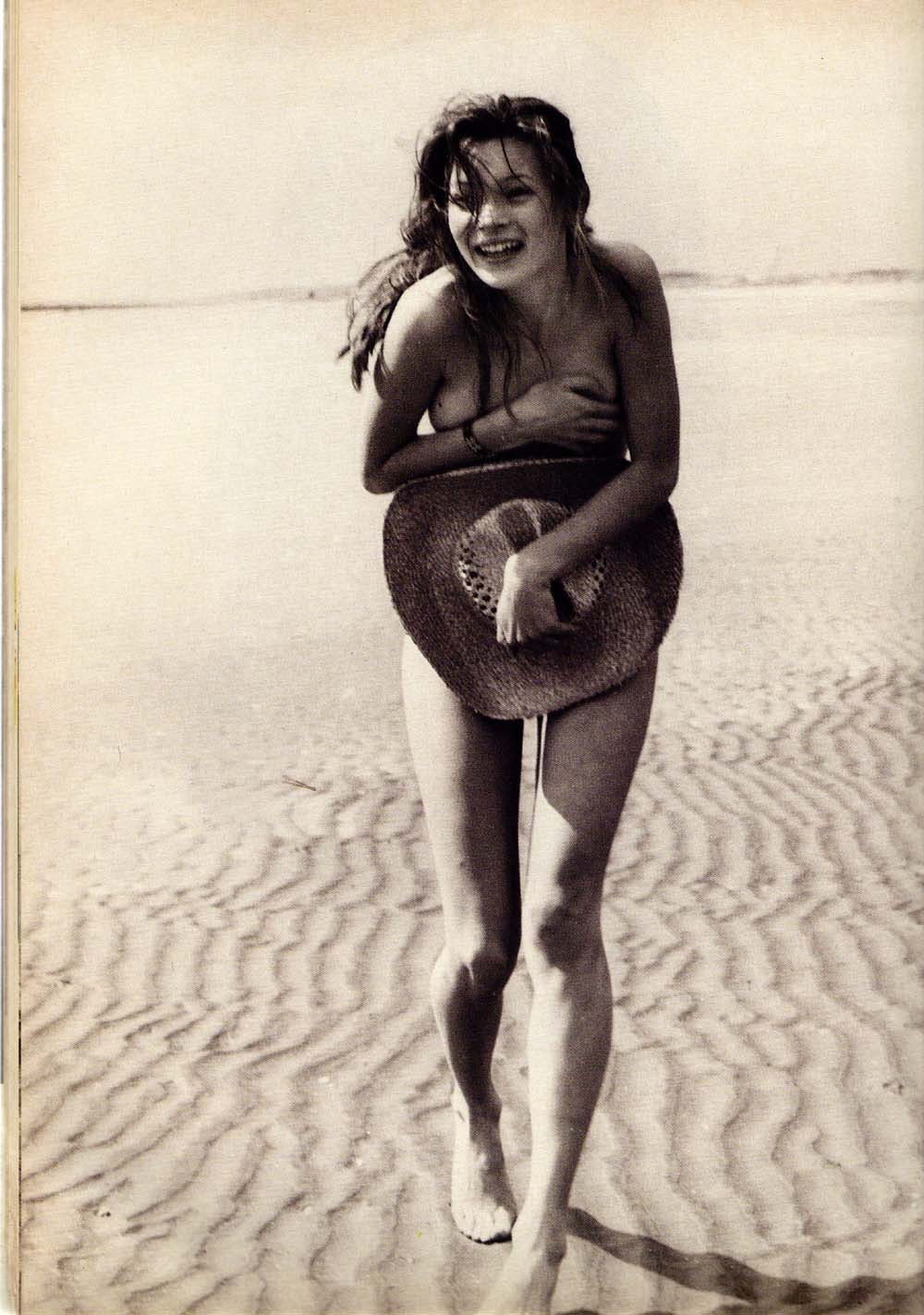


Pictures above by Corinne Day for The Face magazine, July 1990
Over the ocean, grunge bands expressed their dissatisfaction and in Manchester the youth tuned out in the reviving sounds of psychedelia of bands such as The Stone Roses, The Charlatans and The Happy Mondays. Kate’s “elegantly waisted” look was perfect for Corinne Day’s aims in photography, for her love of realism. A new philosophy required a new look, and strong, over the top and glamorous models of the 1980s were passé. Just like Egon Schiele in his nudes and self-portraits, Corinne Day’s photographs penetrate to the bare essence and expose the truth, and what lies within. Schiele freed the women from Klimt’s suffocating gold and poisonous flowers, and focused on the psychology of their faces. In a similar way, Day freed the model from the excessiveness of shoulder pads and too much blush. Calvin Klein said “For me, Kate’s body represented closing the door on the excessiveness of the ’80s”.
Here is an expert from Maureen Callahan’s book “Champagne Supernovas“: “The culture at large didn’t see Kate that way. Up against the skyscraper supermodels of the ’80s, their very perfection a comment on American supremacy, a small-boned, flat-chested model like Kate Moss was heresy. Someone her size hadn’t been seen since Twiggy in the ’60s; suddenly, Kate and Calvin Klein were accused of promoting anorexia, heroin use, child pornography, and the downfall of Western civilization. She was on the sides of buses, kiosks, and pay phones, naked and draped across a velvet sofa in a ramshackle room, “FEED ME” often scrawled across the ad by protesters.”
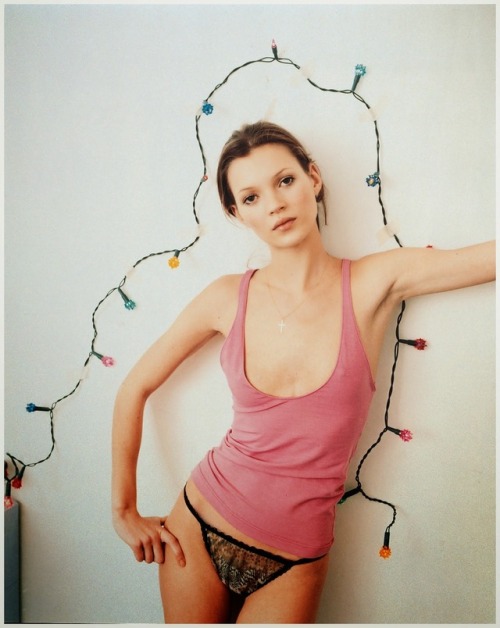

Under Exposure, Kate Moss by Corinne Day for Vogue UK, June 1993
Here is another interesting passage from Callahan’s book “Champagne Supernovas” about Corinne Day’s photo shoot with Kate Moss: “When British Vogue commissioned Corinne for a lingerie shoot with Kate, Corinne insisted on creative control. She shot in Kate’s London apartment and staged it to look like her own flat: modest and cold, with white walls and gray carpet, exposed wiring, a mattress on the floor. Kate had been crying after a fight with her boyfriend, and Corinne exploited the juxtaposition of distress and seduction, putting Kate in tiny cotton tanks and silk underwear, some of it from a sex shop on Brewer Street. In the finished editorial, Kate, silhouetted by a string of multicolored Christmas lights, looked frail and lost.”

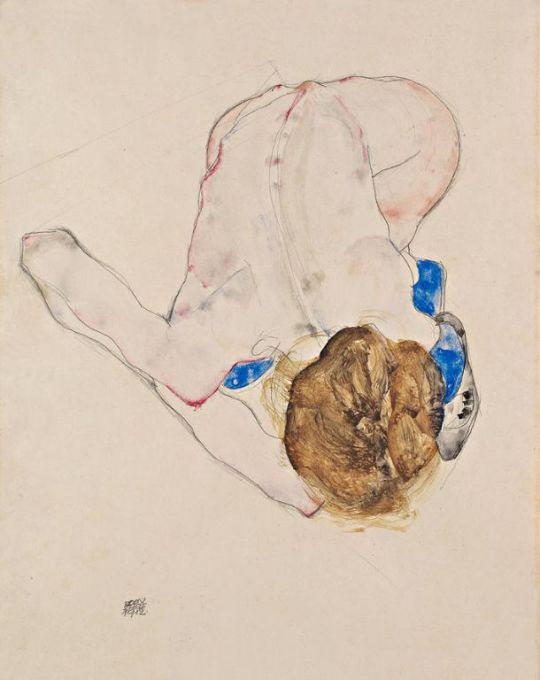
Egon Schiele, Nude With Blue Stockings Bending Forward, 1912
To end, here are some lyrics from the song which inspired me to write this post in the first place: “Lipgloss” by Pulp:
No wonder you’re looking thin,
When all that you live on is lipgloss and cigarettes.
And scraps at the end of the day when he’s given the rest,
To someone with long black hair.
All those nights up making such a mess of the bed.
Oh you never ever want to go home.

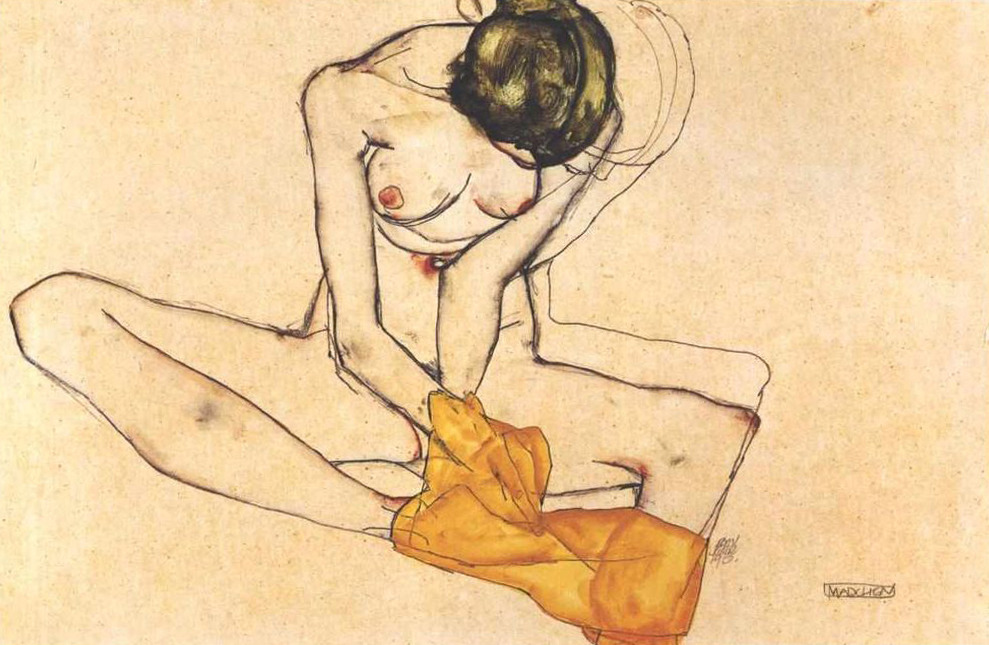
Egon Schiele, Sitting Female Nude with Yellow Blanket, 1910
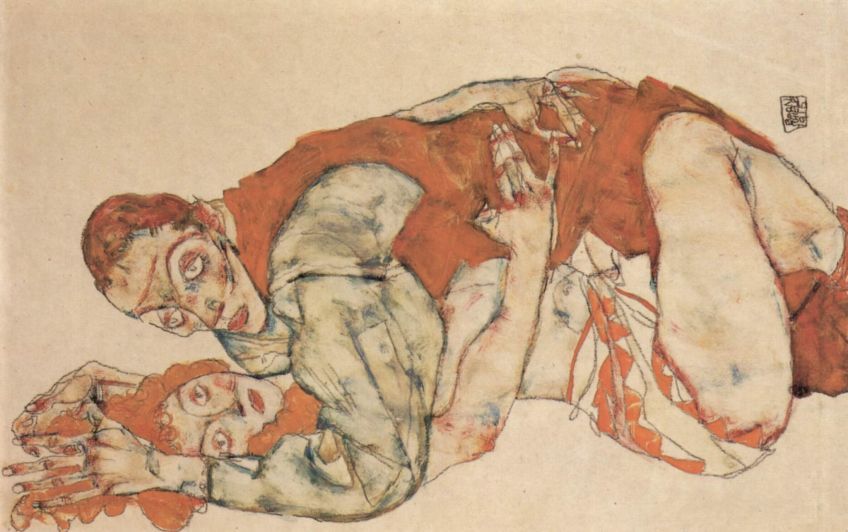
Egon Schiele, Lovemaking, 1915

Kate Moss and Johnny Depp by Annie Leibovitz, 1994

Egon Schiele, Lovers – Self-Portrait With Wally, c. 1914-1915, gouache and pencil on paper
Tags: 1910s, 1990s, art, Austrian art, body ideal, Corinne Day, drawings, Egon Schiele, eleganty wasted, fashion, fashion photography, grunge, heroin chic, Kate Moss, lipgloss and cigarettes, London, model, nihilism, Nude, Photography, Pulp, skinny, Vienna
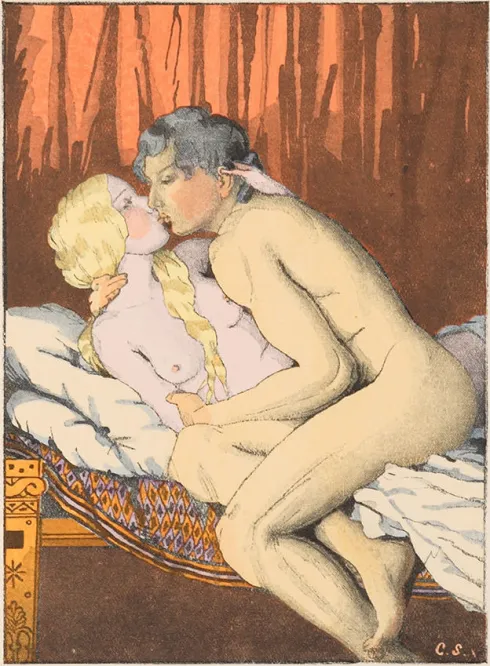
 Konstantin Somov, The Lovers, 1933
Konstantin Somov, The Lovers, 1933