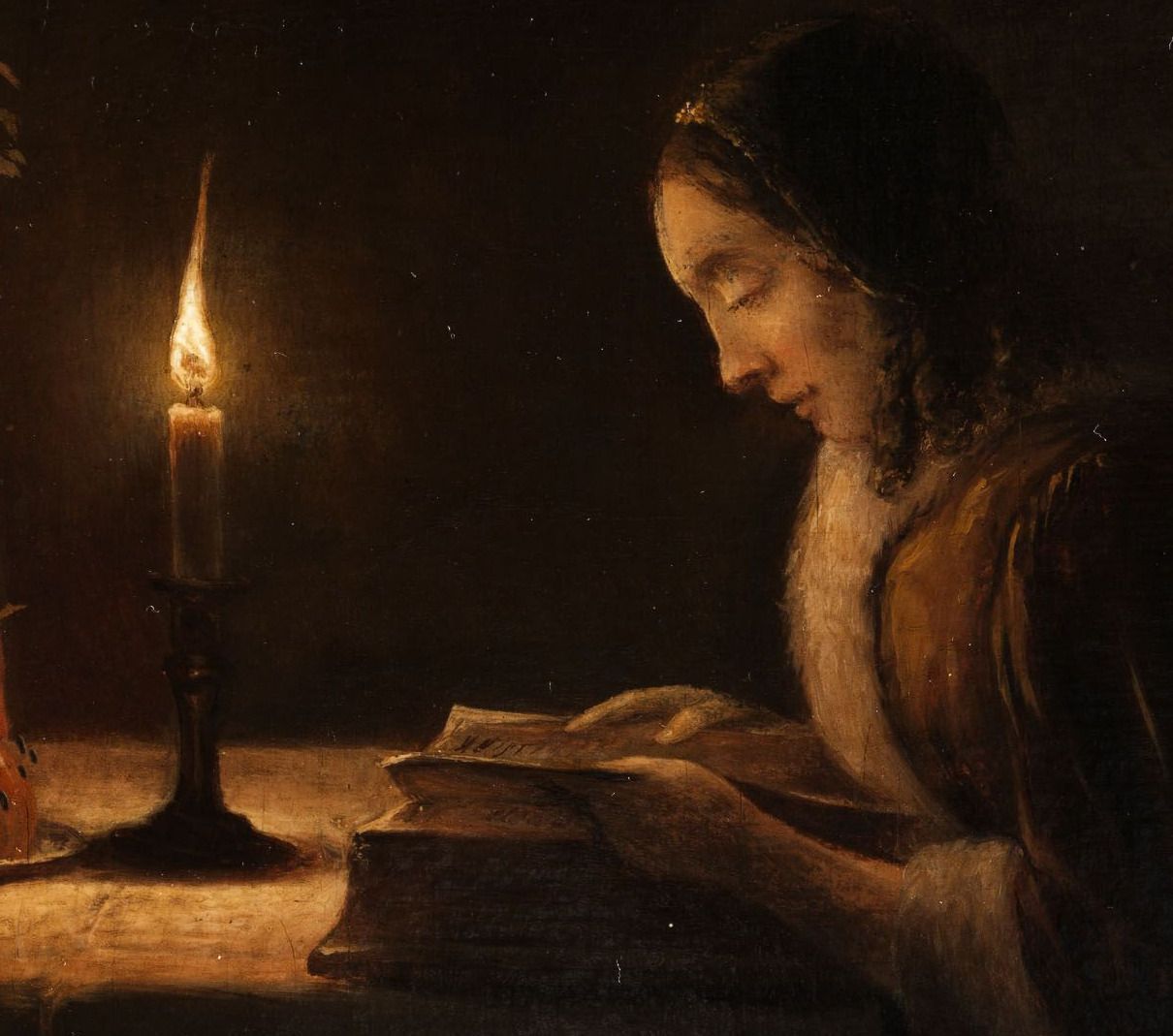
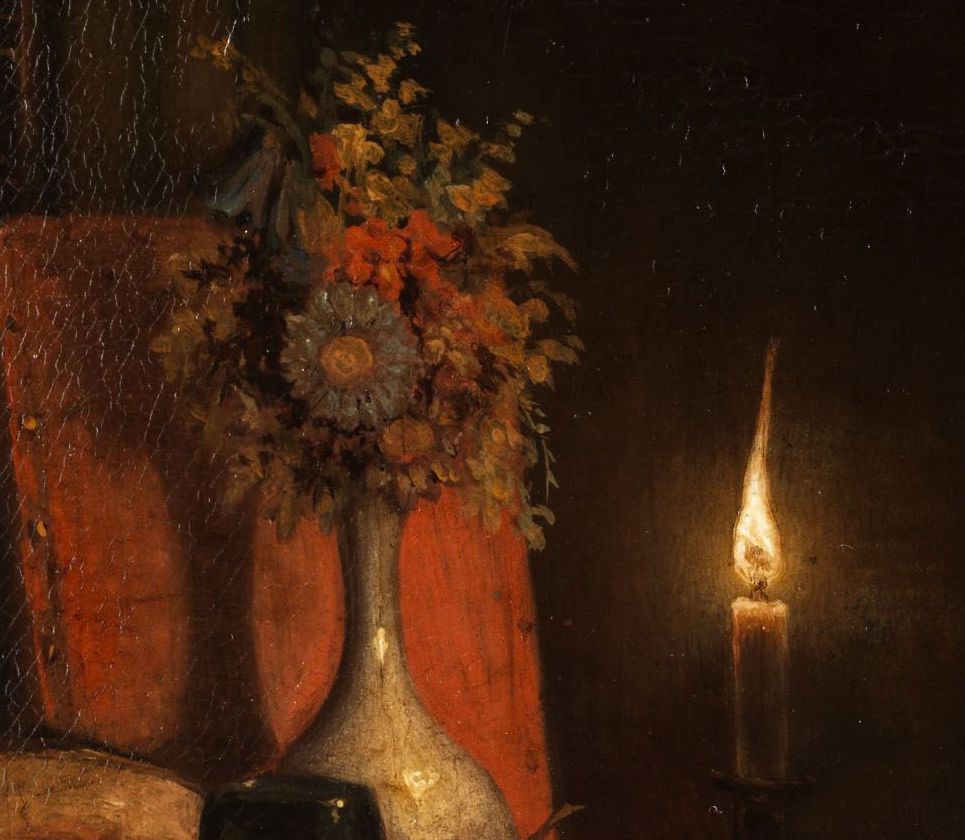“The Arlesian sun smote Vincent between the eyes, and broke him wide open. It was a whirling, liquid ball of lemon-yellow fire, shooting across a hard blue sky and filling the air with blinding light. The terrific heat and intense clarity of the air created a new and unfamiliar world.”
(Irving Stone, Lust for Life)
 Vincent Van Gogh, Still Life: Vase with Fourteen Sunflowers, August 1888
Vincent Van Gogh, Still Life: Vase with Fourteen Sunflowers, August 1888
One of my greatest joys in these early spring days is noticing and gazing at the trees in bloom, the same trees which were sad-looking and bare for months, and enjoying the golden rays of sun caressing me and promising ever warmer days. The joy of feeling the warm sun on your skin cannot be put in words! When it comes to art, my mind instantly went to Vincent van Gogh’s sunflowers, his delicate almond blossoms and blooming orchards, I need his yellows and blues like I need the air to breathe. I was reading some of his letter again and also I was rereading Irving Stone’s wonderful novel “Lust for Life”, first published in 1934, which is a romanticised biography of Vincent van Gogh. I really recommend the book to everyone because it’s just so beautifully written and it absolutely sweeps you away. Irving Stone was just a great writer, I also read his novel “Agony and Ecstasy” about the life of Michelangelo, and I loved it as well, and I am not even interested in the art of Michelangelo and I think that speaks for the brilliancy of Stone’s writing. So, I decided to share passages from the novel which I found particularly interesting and accompany it with Van Gogh’s paintings and my own thoughts. After spending some time in Paris and living with his brother, Vincent, a man from the drab north, felt an inexplicable aching and longing for sun and in spring of 1888 he arrived to Arles, a small town in Provence, and that is where some of his most exciting, most vibrant paintings were painted. Here is how his arrival and first impressions of Arles are described in “Lust for Life”:
“He dropped out of the third-class carriage early in the morning and walked down the winding road that led from the station to the Place Lamartine, a market square bounded on one side by the embankment of the Rhône, on the other by cafés and wretched hotels. Arles lay straight ahead, pasted against the side of a hill with a neat mason’s trowel, drowsing in the hot, tropical sun. When it came to looking for a place to live, Vincent was indifferent. He walked into the first hotel he passed in the Place, the Hotel de la Gare, and rented a room. It contained a blatant brass bed, a cracked pitcher in a washbowl, and an odd chair. The proprietor brought in an unpainted table. There was no room to set up an easel, but Vincent meant to paint out of doors all day.
He threw his valise on the bed and dashed out to see the town. There were two approaches to the heart of Arles from the Place Lamartine. The circular road on the left was for wagons; it skirted the edge of the town and wound slowly to the top of the hill, passing the old Roman forum and amphitheatre on the way. Vincent took the more direct approach, which led through a labyrinth of narrow cobblestone streets. After a long climb he reached the sun scorched Place de la Mairie. On the way up he passed cold stone courts and quadrangles which looked as though they had come down untouched from the early Roman days. In order to keep out the maddening sun, the alleys had been made so narrow that Vincent could touch both rows of houses with outstretched fingertips. To avoid the torturing mistral, the streets wound about in a hopeless maze on the side of the hill, never going straight for more than ten yards. There was refuse in the streets, dirty children in the doorways, and over everything a sinister, hunted aspect.

Vincent van Gogh, Peach Tree in Blossom, Arles, April-May 1888
Vincent left the Place de la Mairie, walked through a short alley to the main marketing road at the back of the town, strolled through the little park, and then stumbled down the hill to the Roman arena. He leaped from tier to tier like a goat, finally reaching the top. He sat on a block of stone, dangled his legs over a sheer drop of hundreds of feet, lit his pipe, and surveyed the domain of which he had appointed himself lord and master.
The town below him flowed down abruptly to the Rhône like a kaleidoscopic waterfall. The roofs of the houses were fitted into each other in an intricate design. They had all been tiled in what was originally red clay, but the burning, incessant sun had baked them to a maze of every colour, from the lightest lemon and delicate shell pink to a biting lavender and earthy loam-brown.
The wide, rapidly flowing Rhône made a sharp curve at the bottom of the hill on which Arles was plastered, and shot downward to the Mediterranean. There were stone embankments on either side of the river. Trinquetaille glistened like a painted city on the other bank. Behind Vincent were the mountains, huge ranges sticking upward into the clear white light. Spread out before him was a panorama of tilled fields, of orchards in blossom, the rising mound of Montmajour, fertile valleys ploughed into thousands of deep furrows, all converging at some distant point in infinity.

Vincent van Gogh, Blossoming Almond Branch in a Glass, 1888
But it was the colour of the country-side that made him run a hand over his bewildered eyes. The sky was so intensely blue, such a hard, relentless, profound blue that it was not blue at all; it was utterly colorless. The green of the fields that stretched below him was the essence of the colour green, gone mad. The burning lemon-yellow of the sun, the blood-red of the soil, the crying whiteness of the lone cloud over Montmajour, the ever reborn rose of the orchards… such colourings were incredible. How could he paint them? How could he ever make anyone believe that they existed, even if he could transfer them to his palette? Lemon, blue, green, red, rose; nature run rampant in five torturing shades of expression.
Vincent took the wagon road to the Place Lamartine, grabbed up his easel, paints, and canvas and struck out along the Rhône. Almond trees were beginning to flower everywhere. The glistening white glare of the sun on the water sent stabs of pain into his eyes. He had left his hat in the hotel. The sun burned through the red of his hair, sucked out all the cold of Paris, all the fatigue, discouragement, and satiety with which city life had glutted his soul.
A kilometre down the river he found a drawbridge with a little cart going over it, outlined against a blue sky. The river was as blue as a well, the banks orange, coloured with green grass. A group of washerwomen in smocks and many-coloured caps were pounding dirty clothes in the shade of a lone tree. Vincent set up his easel, drew a long breath, and shut his eyes. No man could catch such colourings with his eyes open. There fell away from him Seurat’s talk about scientific pointillism, Gauguin’s harangues about primitive decorativeness, Cezanne’s appearances beneath solid surfaces, Lautrec’s lines of colour and lines of splenetic hatred.“